29 Aug 2018 by AXXELIS
How to make the gene-editing tool CRISPR work even better
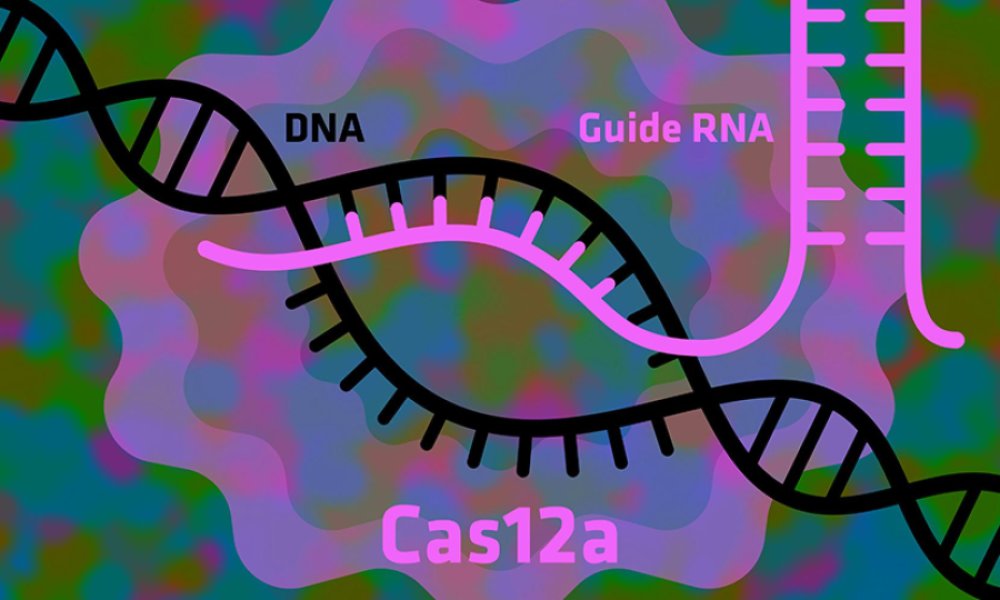
Scientists have found conclusive evidence that Cas9, the most popular enzyme currently used in CRISPR gene editing, is less effective and precise than one of the lesser-used CRISPR proteins, Cas12a. Because Cas9 is more likely to edit the wrong part of a plant’s or animal’s genome, disrupting healthy functions, the scientists make the case that switching to Cas12a would lead to safer and more effective gene editing.
Predicting the response to immunotherapy using artificial intelligence
A study published in The Lancet Oncologyestablishes for the first time that artificial intelligence can process medical images to extract biological and clinical information. By designing an algorithm and developing it to analyse CT scan images, medical researchers at Gustave Roussy, CentraleSupélec, Inserm, Paris-Sud University and TheraPanacea (spin-off from CentraleSupélec specialising in artificial intelligence in oncology-radiotherapy and precision medicine) have created a so-called radiomic signature. This signature defines the level of lymphocyte infiltration of a tumour and provides a predictive score for the efficacy of immunotherapy in the patient.